Microcontroller projects
Oscilloscope clock with internet time
last updated: 2023-09-28
Quick links
- Introduction
- Oscilloscope clock with Teensy 3.6
- Oscilloscope clock with ESP32
- 3D printed housing
- Downloads

Introduction
Old Oscilloscopes want to live forever. To do so, here is the oscilloscope clock. The code is written to get a clear image of a clock with no ghost lines. The hands are drawn beginning from the origin and back to the origin. Strokes are drawn during drawing the circle.
Teensy 3.6 with internal RTC is quick enough to use mathematical functions. With his two 12-bit DAC, the picture is rock stable and sharp. The only hardware needed is an external battery for the RTC. (code: osciclock_teensy36_without_esp.ino).
The Teensy has no direct connection to the Internet and no DCF77, so the time may be getting imprecise over the year. So the best solution is the Teensy with an ESP8266 or ESP32 to get time updates from an NTP server (code: osciclock_teensy36_ntp_v5.ino for the teensy and osciclock_teensy36_esp_ntp_2_serial.ino for the ESP).
An ESP8266 or ESP32 is sending once an hour the time to the Teensy over hardware Serial1 or Serial2. If synchronising the text "NTP" is displayed for 10 seconds on the oscilloscope screen.
The ESP32 has also two DAC with 8 bit and the possibility to get the time over NTP, but it is not quick enough to use mathematical functions because of his operating system running in background (RTOS). It was even necessary to create tables for the circle and the hands and to reduce the points of the circle to 180 to get a more stable non flickering image (code: osciclock_esp32_tab.ino).
Oscilloscope clock with Teensy 3.6
Teensy 3.6 has an internal RTC (and crystal) and 2 DAC with 12 bit. So no other hardware is needed then the Teensy-Board to create a nice oscilloscope clock.
All the magic is in the code. The Teensy is quick enough to calculate the needed points for the clock, so we can omit tables. The clock strokes are drawn from the circle line back and forth, so no ghost lines appear. Same thing for the second line and hands. The resolution can be changes from 8 bit to 12 bit. 12 bit gets a real sharp, steady nice image of the clock.
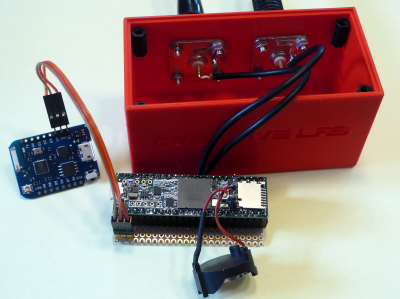
The best solution is adding an ESP8266 to get NTP from Internet. The ESP8266 is sending once an hour the time to the Teensy.
Here is the Arduino code with ESP8266 (D4, TXD) connected to pin1 (RXD1) for the Teensy and the ESP8266.
The code (also code for Teensy without ESP) can be found on git: https://github.com/weigu1/osciclock.
/* oscilloscope clock with teensy 3.6
* osciclock_teensy36_ntp_v5.ino
* weigu.lu
* v5 with NTP over serial
* 2021-05-16
*/
#include <TimeLib.h> //https://www.pjrc.com/teensy/td_libs_Time.html
#define DEBUG
const byte DAC1 = A21;
const byte DAC2 = A22;
const float PI_8 = 3.14159265;
const byte DAC_RESOLUTION = 12; // dac DAC_RESOLUTIONolution in bit
int r = (pow(2,DAC_RESOLUTION)-2)/2; // max circle radius
int rs = r*0.80; // radius seconds
int rm = r*0.85; // radius minutes
int rh = r*0.65; // radius hours
int rst = r*0.95; // radius strokes
int rstm = r*0.90; // radius main strokes
int hands = 5; // fraction where to split the hand
int handam = 12; // angle (width) of hand (min)
int handah = 20; // angle (width) of hand (hour)
byte NTP_flag = 0;
unsigned long flag_time = millis();
void setup() {
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Debugging started!");
#endif
Serial1.begin(115200);
setSyncProvider(getTeensy3Time); // set the time library to use RTC
analogWriteResolution(DAC_RESOLUTION);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial1.available()) {
time_t t = processSyncMessage();
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.println("Data available, epoch time: " + String(t));
#endif
if (t != 0) {
Teensy3Clock.set(t); // set the RTC
setTime(t);
NTP_flag = 1;
flag_time = millis();
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.println("NTP Flag: " + String(NTP_flag));
#endif
}
}
circle(); // draw a circle
sec_line(second()); // draw the sec hand
min_line(minute()); // draw the minute hand
hour_line(hour(),minute(),second()); // draw the hour hand
display_weigu(r*15/10,r/32,r/64); // draw weigu.lu
if (NTP_flag) { // show that clock is syncing
display_NTP(r*18/10,r*19/10,r/64);
if ((millis()-flag_time) > 10000) { //clear after 10 seconds
NTP_flag = 0;
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.println("NTP Flag: " + String(NTP_flag));
#endif
flag_time = millis();
}
}
}
time_t getTeensy3Time() {
return Teensy3Clock.get();
}
void point(int x,int y) {
analogWrite(DAC1, y);
analogWrite(DAC2, x);
}
void line (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) { // draw a line between 2 points
int d = sqrt(((x2-x1)*(x2-x1))+((y2-y1)*(y2-y1)));
int steps = d/4;
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++) {
point(x1+i*(x2-x1)/steps,y1+i*(y2-y1)/steps);
}
}
void dline (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) { // draw a line back and forth
int d = sqrt(((x2-x1)*(x2-x1))+((y2-y1)*(y2-y1)));
int steps = d/4;
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++) {
point(x1+i*(x2-x1)/steps,y1+i*(y2-y1)/steps);
}
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++) { //draw line backwards to avoid ghosts
point(x2+i*(x1-x2)/steps,y2+i*(y1-y2)/steps);
}
}
void hand (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2, int angle) { // draw a hand between 2 points
int d = sqrt(((x2-x1)*(x2-x1))+((y2-y1)*(y2-y1)));
int ds = d/hands;
int ao = round( atan2 (y2-y1,x2-x1)*180/PI_8 );
int a1 = ao+angle;
int a2 = ao-angle;
int p1x = x1+ds*cos(a1*PI_8/180);
int p1y = y1+ds*sin(a1*PI_8/180);
int p2x = x1+ds*cos(a2*PI_8/180);
int p2y = y1+ds*sin(a2*PI_8/180);
line (x1,y1,p1x,p1y);
line (p1x,p1y,x2,y2);
line (x2,y2,p2x,p2y);
line (p2x,p2y,x1,y1);
}
void circle() { //function to draw a circle
for(int i=0;i<=360;i++) {
int circlex = r*cos(i*PI_8/180)+r;
int circley = r*sin(i*PI_8/180)+r;
point(circlex,circley);
if (i%6==0) { // min lines
if (i%30==0) { // 5 min lines
dline(circlex,circley,rstm*cos(i*PI_8/180)+r,rstm*sin(i*PI_8/180)+r);
}
else {
dline(circlex,circley,rst*cos(i*PI_8/180)+r,rst*sin(i*PI_8/180)+r);
}
}
}
}
void sec_line(int second) {
int angle = ((60-second)*6+90)%360;
dline(r,r,rs*cos(angle*PI_8/180)+r,rs*sin(angle*PI_8/180)+r);
}
void min_line(int minute) {
int angle = ((60-minute)*6+90)%360;
hand(r,r,rm*cos(angle*PI_8/180)+r,rm*sin(angle*PI_8/180)+r,handam);
}
void hour_line(int hour, int minute, int second) {
if (hour>12) {
hour = hour-12;
}
int hours = hour*3600 + minute*60 + second;
int angle = ((43200-hours)/120+90)%360;
hand(r,r,rh*cos(angle*PI_8/180)+r,rh*sin(angle*PI_8/180)+r,handah);
}
void display_weigu(int x1, int y1, int s) {
int h = 5*s; // height of chars
int w = 5*s; // width of chars
int d = 2*s; // distance between chars
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1,x1+w/2,y1+h/2);
line(x1+w/2,y1+h/2,x1+w,y1);
line(x1+w,y1,x1+w,y1+h);
x1 = x1+w+d;
w = w*3/5;
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1+h,x1+w,y1+h);
line(x1+w,y1+h,x1+w,y1+h/2);
line(x1+w,y1+h/2,x1,y1+h/2);
line(x1,y1,x1+w,y1);
x1 = x1+w+d;
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h*3/4);
point(x1,y1+h);
point(x1+1,y1+h);
point(x1+1,y1+1+h);
point(x1,y1+1+h);
x1 = x1+d;
line(x1+w,y1,x1,y1);
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1+h,x1+w,y1+h);
line(x1+w,y1+h,x1+w,y1);
line(x1+w,y1,x1+w,y1-h/2);
line(x1+w,y1-h/2,x1,y1-h/2);
x1 = x1+w+d;
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1,x1+w,y1);
line(x1+w,y1,x1+w,y1+h);
x1 = x1+w+d;
point(x1,y1);
point(x1+1,y1);
point(x1+1,y1+1);
point(x1,y1+1);
x1 = x1+d;
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+1.5*h);
x1 = x1+d;
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1,x1+w,y1);
line(x1+w,y1,x1+w,y1+h);
}
void display_NTP(int x1, int y1, int s) {
int h = 5*s; // height of chars
int w = 3*s; // width of chars
int d = 2*s; // distance between chars
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1+h,x1+w,y1);
line(x1+w,y1+h,x1+w,y1);
x1 = x1+w+d;
//w = w*3/5;
line(x1+w/2,y1,x1+w/2,y1+h);
line(x1+w/2,y1+h,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1+h,x1+w,y1+h);
line(x1+w,y1+h,x1+w/2,y1+h);
line(x1+w/2,y1+h,x1+w/2,y1);
x1 = x1+w+d;
line(x1,y1,x1,y1+h);
line(x1,y1+h,x1+w,y1+h);
line(x1+w,y1+h,x1+w,y1+h/2);
line(x1+w,y1+h/2,x1,y1+h/2);
line(x1,y1+h/2,x1,y1);
}
/* code to process time sync messages from the serial port pjrc.com */
#define TIME_HEADER "T" // Header tag for serial time sync message
unsigned long processSyncMessage() {
unsigned long pctime = 0L;
const unsigned long DEFAULT_TIME = 1603037307; // 2020-10-20
if(Serial1.find(TIME_HEADER)) {
pctime = Serial1.parseInt();
serial1_in_flush(); // remove CR or LF
return pctime;
if( pctime < DEFAULT_TIME) { // check the value is a valid time (greater than 2020-10-20)
pctime = 0L; // return 0 to indicate that the time is not valid
}
}
serial1_in_flush();
return pctime;
}
void serial1_in_flush() {
while(Serial1.available() > 0) {
Serial1.read();
}
}
Here the code for the ESP sending the time over serial:
/*
osciclock_teensy36_esp_ntp_2_serial.ino
ESP8266: Sending NTP time over hardware Serial (Serial1 or Serial2 (ESP32))
weigu.lu
for more infos look here:
http://weigu.lu/microcontroller/tips_tricks/esp_NTP_tips_tricks/index.html
*/
#ifdef ESP8266 // all includes are from Arduino Core, no external lib
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
// <time.h> and <WiFiUdp.h> not needed. already included by core.
#else
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <time.h>
#endif
// The file "secrets.h" has to be placed in the sketchbook libraries folder
// in a folder named "Secrets" and must contain your secrets e.g.:
// const char *MY_WIFI_SSID = "mySSID"; const char *MY_WIFI_PASSWORD = "myPASS";
#define USE_SECRETS
#define DEBUG
#define HSERIAL Serial1
/****** WiFi and network settings ******/
#ifdef USE_SECRETS
#include <secrets.h>
const char *WIFI_SSID = MY_WIFI_SSID;
const char *WIFI_PASSWORD = MY_WIFI_PASSWORD; // password
#else
const char* *WIFI_SSID = mySSID; // if no secrets file, add your SSID here
const char* *WIFI_PASSWORD = myPASSWORD; // if no secrets file, add your PASS here
#endif
/****** NTP settings ******/
const char *NTP_SERVER = "lu.pool.ntp.org";
// your time zone (https://remotemonitoringsystems.ca/time-zone-abbreviations.php)
const char *TZ_INFO = "CET-1CEST-2,M3.5.0/02:00:00,M10.5.0/03:00:00";
const char *TZ_INFO_UTC = "CET0CEST0";
time_t now, now2;
tm timeinfo; // time structure
void setup() {
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("\nHello");
#endif
HSERIAL.begin(115200);
init_ntp_time();
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(200);
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.print ( "." );
#endif
}
time(&now); // this function calls the NTP server only every hour
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.println("\nConnected to SSID " + WiFi.SSID() + " with IP " +
WiFi.localIP().toString() + "\nSignal strength is " +
WiFi.RSSI() + " dBm\n");
Serial.println("Epoch time (UTC): " + String(now));
Serial.println("Setup done!");
#endif
}
void loop() {
time(&now); // this function calls the NTP server only every hour
setenv("TZ", TZ_INFO, 1); // set environment variable with your time zone
tzset();
localtime_r(&now, &timeinfo);
setenv("TZ", TZ_INFO_UTC, 1); // set environment variable UTC:
tzset(); // trick to force mktime to deliver what we need
now2 = mktime(&timeinfo);
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.println('T' + String(now2));
#endif
HSERIAL.println('T' + String(now2));
delay(3600000);
}
// init NTP time: call this before the WiFi connect!
void init_ntp_time() {
#ifdef ESP8266
configTime(TZ_INFO, NTP_SERVER);
#else
configTime(0, 0, NTP_SERVER); // 0, 0 because we will use TZ in the next line
setenv("TZ", TZ_INFO, 1); // set environment variable with your time zone
tzset();
#endif
}
Oscilloscope clock with ESP32
The ESP32 (WEMOS32) does not need additional components. Tables are used to enhance speed.

Her is the Arduino code (on git: https://github.com/weigu1/osciclock):
/* oscilloscope clock with wemos WEMOS32 (esp32)
* osciclock_esp32_tab.ino
* weigu.lu
* (reduce upload speed if errors occur)
* for tables see libreoffice calc sheet
* DAC 1 = Pin 25, DAC_2 = Pin 26;
*/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include "time.h"
#include <driver/dac.h>
const char* ssid = "myssid";
const char* password = "mypass";
const char* ntpServer = "pool.ntp.org";
const long gmtOffset_sec = 3600;
const int daylightOffset_sec = 3600;
struct tm ti;
// sine and cosine table with 360 points
unsigned int circlex[]={
255,255,255,255,255,255,254,254,
...
};
unsigned int circley[]={
128,130,132,134,136,139,141,143,
...
};
// 5 min strokes
unsigned int min5linesxy[]={
243,128,227,185,185,227,128,243,
...
};
// seconds hand r = 102 (80%)
unsigned int secHandxy[]={
128,230,117,229,106,227,96,225,
...
};
// minute hand r = 108 (85%) fraction = 5 angle = 12
unsigned int minHand[]={
128,236,123,149,132,149,
...
};
// hour hand r = 83 (65%) fraction = 5 angle = 20
unsigned int hourHand[]={
128,211,122,143,133,143,
...
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
dac_output_enable(DAC_CHANNEL_1);
dac_output_enable(DAC_CHANNEL_2);
//connect to WiFi
Serial.printf("Connecting to %s ", ssid);
WiFi.enableSTA(true);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println(" CONNECTED");
//init and get the time
configTime(gmtOffset_sec, daylightOffset_sec, ntpServer);
getLocalTime(&ti);
WiFi.disconnect(true); //disconnect WiFi as it's no longer needed
WiFi.mode(WIFI_OFF);
}
void loop() {
getLocalTime(&ti);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
circle(); // function to make a circle
sec_hand(ti.tm_sec);
min_hand(ti.tm_min);
hour_hand(ti.tm_hour,ti.tm_min);
}
// Reset time at 4 in the morning
if ((ti.tm_hour == 4) and (ti.tm_min == 0) and (ti.tm_sec == 0)) {
ESP.restart();
}
}
void point(int x,int y) {
dac_output_voltage(DAC_CHANNEL_1, y);
dac_output_voltage(DAC_CHANNEL_2, x);
}
void line (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2, int steps) { // draw a line between 2 points
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++) {
point(x1+i*(x2-x1)/steps,y1+i*(y2-y1)/steps);
}
}
void dline (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int steps) { // draw a line back and forth
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++) {
point(x1+i*(x2-x1)/steps,y1+i*(y2-y1)/steps);
}
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++) { //draw line backwards to avoid ghosts
point(x2+i*(x1-x2)/steps,y2+i*(y1-y2)/steps);
}
}
void circle() { //function to draw a circle
for(int i=0;i<360;i=i+2) {
point(circlex[i],circley[i]);
if (i%30==0) { // 5 min lines
dline(circlex[i],circley[i],min5linesxy[i/30*2],min5linesxy[i/30*2+1],5);
}
}
}
void sec_hand(int second) {
int i = (60-second);
if (i == 60) i = 0;
i = i*2;
dline(127,127,secHandxy[i],secHandxy[i+1],30);
}
void min_hand(int minute) {
int i = (60-minute);
if (i == 60) i = 0;
i = i*6;
line (127,127,minHand[i+2],minHand[i+3],10);
line (minHand[i+2],minHand[i+3],minHand[i],minHand[i+1],40);
line (minHand[i],minHand[i+1],minHand[i+4],minHand[i+5],40);
line (minHand[i+4],minHand[i+5],127,127,10);
}
void hour_hand(int hour, int minute) {
if (hour>12) hour = hour-12;
int hours = (hour*5 + (minute/12));
int i = (60-hours);
if (i == 60) i = 0;
i = i*6;
line (127,127,hourHand[i+2],hourHand[i+3],7);
line (hourHand[i+2],hourHand[i+3],hourHand[i],hourHand[i+1],30);
line (hourHand[i],hourHand[i+1],hourHand[i+4],hourHand[i+5],30);
line (hourHand[i+4],hourHand[i+5],127,127,7);
}
3D printed housing
Find the freecad file and the stl files under Downloads. I used 4 hole flange mount BNCs from my stock with 19 mm distance between the holes. Perhaps you have to adjust the distance in the freecad file.
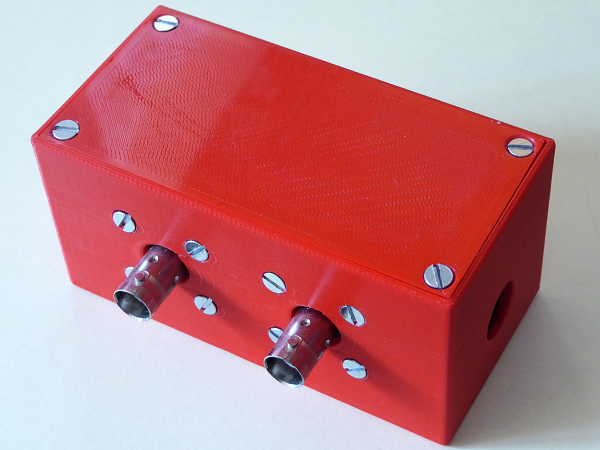

The little piece of breadboard that holds the teensy is glued with hot glue to the bottom of the case.
Downloads
Everything is on git: https://github.com/weigu1/osciclock.
