Microcontroller projects
LoRa P2P with ESP8266 or ESP32 and the SX1276 from SEMTECH
last updated: 2024-03-02
Quick links
Intro
LoRa was developped by SEMTECH. We will use here their simple LoRa chip SX1276, that can be bought on a breakout board RFM95W-V2.0 from hoperf). With an ESP8266 (WEMOS D1 mini (pro) or an ESP32 (MHETLIVE Minikit) and the LoRa library from Sandeep Mistry it is easy to build a LoRa p2p device.
Hardware
Unfortunately the breakout board RFM95W uses a 2 mm pin header pitch instead of the usually used 2.54 mm (0.1 in). So we need an additional breakout board to be able to use the chip on a breadboard.
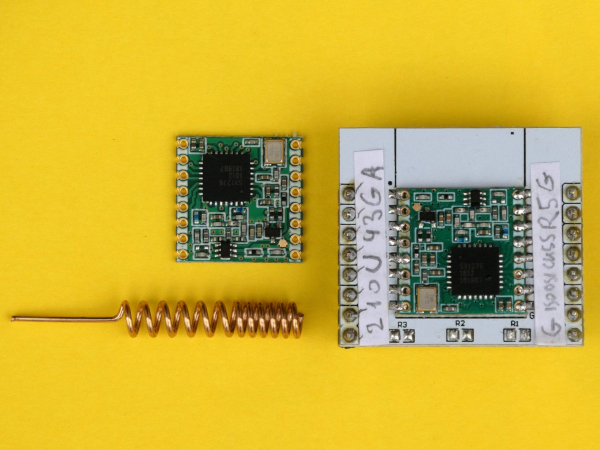
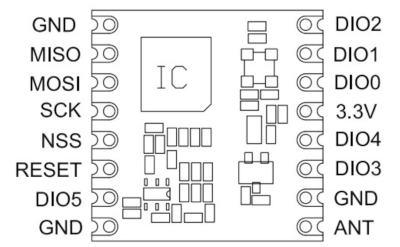
Connections:
Don't forget to connect the antenna before powering the board! Without antenna the board can be damaged!
If you don't have an antenna, use a wire with 8.2 cm in length.
The board uses the SPI interface (MISO, MOSI, SCK, SS (NSS)) to communicate with the microcontroller, and it is powered with 3.3 V (GND, +3.3 V).
For SPI we usually use the pins of the default SPI interface for MISO, MOSI and SCK. With the function SPI.begin() it is possible to change if a second interface is available. The chip select pin is freely selectable. The library uses by default pin 5. The DI00 pin (RFM95W) must be connected to a pin supporting interrupts, because the LoRa chip signals an incoming message with this output to the microcontroller (default pin 2). Same for DI01, needed only for LoRaWAN (default pin 6). An output pin of the microcontroller can also be used to reset (RESET pin) the LoRa chip if needed.
| LoRa board | Arduino Uno (3V!) | ESP8266 (WEMOS) | ESP32 (MHETLIVE Minikit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3V (Vin) | 3.3V | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| GND | GND | GND | GND |
| MOSI | 11 | 14 | 23 |
| MISO | 12 | 12 | 19 |
| SCK | 13 | 13 | 18 |
| NSS (SS, CS) | 5 | 16 | 5 |
| RST (Reset) | 9 | not connected | not connected |
| DIO0 (G0, IRQ) | 2 | 15 | 26 |
| DIO1 (G1, IRQ) | 6 (only needed for LoRaWAN!) | (only needed for LoRaWAN!) | (only needed for LoRaWAN!) |
| DIO2-5 | not connected | not connected | not connected |
| ANT | antenna | antenna | antenna |
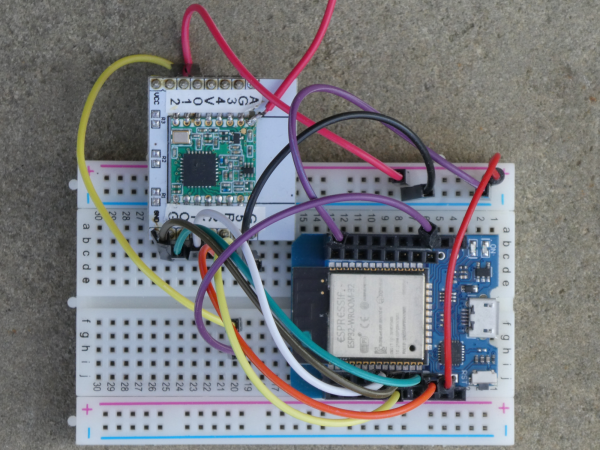
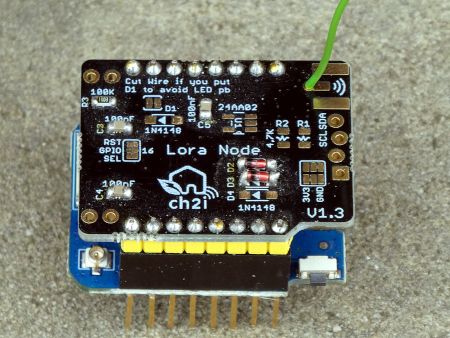
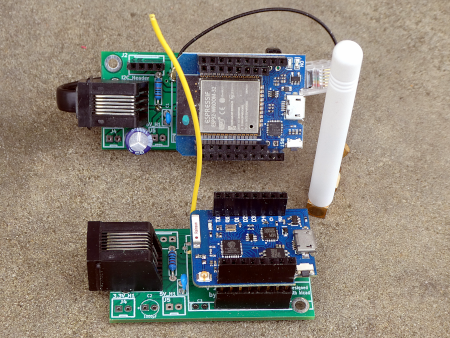
On the net I found an interesting PCB from Charles-Henri Hallard (CH2i) and ordered some PCBs. The version is 1.3. I populated them with only the most necessary components:
RFM95 LoRa breakout, DIO0, DIO1 (only if we need LoRaWAN), C1 (1µF), C2(10µF), R3 (100k).
They work both wit the ESP8266 (WEMOS D1 mini) and the ESP32 (MHETLIVE Minikit) with the same connections as above.
The same connections are also used for the SmartyReader® board v2.2.
Software
We use the LoRa library from Sandeep Mistry. Information about the library can be found in the corresponding LoRa Application Programming Interface (API).
The software can be found on github: https://github.com/weigu1/lora_p2p_SX1276_esp.
Here are two basic sketches for the sender (transmitter):
Sender
/*
lora_p2p_esp_sx1276_simple_sender_868.ino
weigu.lu 2024
ESP32: MH ET LIVE ESP32-MINI-KIT with RFM95W (SX1276)
ESP8266: WEMOS D1 mini pro with RFM95W (SX1276)
MH ET Live |---| Mini Kit WEMOS |---| D1 Mini Pro
GND | RST |---| 3 RxD | GND RST |---| TxD
NC | SVP 36 |---| 1 TxD | 27 A0 |---| RxD
SVN 39 | 26 |---| 22 SCL | 25 D0 16 |---| 5 D1 SCL
35 | SCK 18 |---| 21 SDA | 32 SCK D5 14 |---| 4 D2 SDA
33 | MISO 19 |---| 17 TxD2 | 12 TDI MISO D6 12 |---| 0 D3
34 | MOSI 23 |---| 16 RxD2 | 4 MOSI D7 13 |---| 2 D4 LED
TMS 14 | SS 5 |---| GND | 0 SS D8 15 |---| GND
NC | 3V3 |---| 5V | 2 3V3 |---| 5V
SD2 9 | TCK 13 |---| 15 TD0 | 8 SD1
CMD 11 | SD3 10 |---| 7 SD0 | 6 CLK
LoRa board | ESP8266 | ESP32 |
3.3V (Vin) | 3.3V | 3.3V
GND | GND | GND
MOSI | 14 | 23
MISO | 12 | 19
SCK | 13 | 18
NSS (SS, CS) | 16 | 5
RST (Reset) | nc | 33
DIO0 (G0, IRQ) | 15 | 26
DIO1 (G1, IRQ) | only WAN | only needed for LoRaWAN!
DIO2-5 | nc | not connected (nc)
ANT | antenna | antenna
freq = 868MHz, SPI pins are default pins MOSI=13/23, MISO=12/19, SCK=14/18
*/
#include <SPI.h>
#include <LoRa.h>
#ifdef ESP8266
const byte PIN_SS = 16; // LoRa radio chip select
const byte PIN_RST = -1; // LoRa radio reset (not connected)
const byte PIN_IRQ = 15; // hardware interrupt pin!
#else
const byte PIN_SS = 26;
const byte PIN_RST = -1;
const byte PIN_IRQ = 5;
#endif // #ifdef ESP8266
//const byte PIN_SCK = 18;
//const byte PIN_MISO = 19;
//const byte PIN_MOSI = 23;
unsigned int counter = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("LoRa sender\n");
//SPI.begin(PIN_SCK, PIN_MISO, PIN_MOSI, PIN_SS); // if not default pins
LoRa.setPins(PIN_SS, PIN_RST, PIN_IRQ); // setup LoRa transceiver
if (!LoRa.begin(868E6)) {
Serial.println("Error starting LoRa!");
while (true); // endless loop
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Sending packet number: ");
Serial.println(counter);
LoRa.beginPacket();
LoRa.print("This is packet number ");
LoRa.print(counter);
LoRa.endPacket();
counter++;
delay(60000);
}
Receiver (polling)
/*
lora_p2p_esp_sx1276_simple_receiver_868.ino
The receiver uses polling. Look at the transceiver example for callback.
*/
#include <SPI.h>
#include <LoRa.h>
#ifdef ESP8266
const byte PIN_SS = 16; // LoRa radio chip select
const byte PIN_RST = -1; // LoRa radio reset (not connected)
const byte PIN_IRQ = 15; // hardware interrupt pin!
#else
const byte PIN_SS = 26;
const byte PIN_RST = -1;
const byte PIN_IRQ = 5;
#endif // #ifdef ESP8266
byte packet_size = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("LoRa receiver\n");
LoRa.setPins(PIN_SS, PIN_RST, PIN_IRQ); // setup LoRa transceiver
if (!LoRa.begin(868E6)) {
Serial.println("Error starting LoRa!");
while (true); // endless loop
}
}
void loop() {
packet_size = LoRa.parsePacket(); // try to parse packet
if (packet_size) { // received a packet
Serial.print("Received packet with ");
Serial.print(packet_size);
Serial.print(" byte: '");
while (LoRa.available()) { // read packet
Serial.print((char)LoRa.read());
}
Serial.print("' with RSSI = ");
Serial.print(LoRa.packetRssi());
Serial.println("dBm");
}
}
Transceiver with callback
The following sketch shows how a transceiver can be build with duplex communication and callbacks. Transmitter and receiver use a unique address (only 1 byte = 256 addresses, 0xFF for broadcast messages). The message gets an identifier (ID), realised in the sketch with a simple message counter. The delay time between sends is not static (randomized) to avoid collisions.
/*
lora_p2p_esp_sx1276_transceiver_868.ino
LoRa duplex communication with callback
*/
#include <SPI.h>
#include <LoRa.h>
#ifdef ESP8266
const byte PIN_SS = 16; // LoRa radio chip select
const byte PIN_RST = -1; // LoRa radio reset (not connected)
const byte PIN_IRQ = 15; // hardware interrupt pin!
#else
const byte PIN_SS = 26;
const byte PIN_RST = -1;
const byte PIN_IRQ = 5;
#endif // #ifdef ESP8266
const byte NODE_ADDR = 0x01; // address of this device
const byte GATEWAY_ADDR = 0xFE; // 0xFE=gateway, 0xFF=broadcast
unsigned long send_delay = 60000; // delay in ms between sends
byte msg_out_id = 0; // cnt of outgoing msgs = msg id
byte addr_in_rec, addr_in_sender, msg_in_id, msg_in_length;
String message, msg_out, msg_in, lora_rssi, lora_snr;
volatile bool flag_message_received = false; // flag set by callback
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("LoRa duplex with callback\n");
LoRa.setPins(PIN_SS, PIN_RST, PIN_IRQ); // setup LoRa transceiver
if (!LoRa.begin(868E6)) {
Serial.println("Error starting LoRa!");
while (true); // endless loop
}
LoRa.onReceive(onReceive); // init the callback func.
LoRa.receive(); // start receive mode
}
void loop() {
LoRa.receive(); // go back into receive mode
if (flag_message_received) { // if recv flag set by callback
readMessage();
flag_message_received = false; // set flag back to false
}
if (non_blocking_delay(send_delay)) { // send a message all delay ms
message = "HeLoRa World!";
send_message(message);
Serial.println("Sending:");
Serial.print("GW addr.: ");
Serial.print(GATEWAY_ADDR);
Serial.print(" (1 byte) + node addr.: ");
Serial.print(NODE_ADDR);
Serial.print(" (1 byte) + msg ID: ");
Serial.print(msg_out_id);
Serial.println(" (1 byte) +");
Serial.print("msg length: ");
Serial.print(message.length());
Serial.println(" (1 byte) + message: \"" + message + "\"");
Serial.println("-------------------------------------------------------");
send_delay = send_delay + random(1000); // randomize to avoid collisions
}
delay(1);
}
// callback function
void onReceive(int packetSize) {
if (packetSize == 0) { // if there's no packet, return
return;
}
flag_message_received = true; //Set flag to perform read in main loop
}
// send the message and increment ID
void send_message(String message_out) {
LoRa.beginPacket(); // start packet
LoRa.write(GATEWAY_ADDR); // add destination address
LoRa.write(NODE_ADDR); // add sender address
LoRa.write(msg_out_id); // add message ID (counter)
LoRa.write(message_out.length()); // add payload length
LoRa.print(message_out); // add payload
LoRa.endPacket(); // finish packet and send it
msg_out_id++; // increment message counter (ID)
}
// read a message and check if valid
void readMessage() {
addr_in_rec = LoRa.read(); // recipient address
addr_in_sender = LoRa.read(); // sender address
msg_in_id = LoRa.read(); // incoming msg ID
msg_in_length = LoRa.read(); // incoming msg length
while (LoRa.available()) {
msg_in = LoRa.readString();
yield();
}
if (msg_in_length != msg_in.length()) {// check length for error
Serial.println("error: message length does not match length");
return;
}
if (addr_in_rec != GATEWAY_ADDR && addr_in_rec != 0xFF) {
Serial.println("This message is not for me.");
return;
}
lora_rssi = LoRa.packetRssi();
lora_snr = LoRa.packetSnr();
Serial.print("From: 0x" + String(addr_in_sender, HEX));
Serial.print("\tto: 0x" + String(addr_in_rec, HEX));
Serial.print("\tRSSI: " + lora_rssi);
Serial.println("\tSnr: " + lora_snr);
Serial.print("Message: " + msg_in);
Serial.print("\tLength: " + String(msg_in_length));
Serial.println("\tID: " + String(msg_in_id));
Serial.println("-------------------------------------------------------");
}
// non blocking delay using millis(), returns true if time is up
bool non_blocking_delay(unsigned long milliseconds) {
static unsigned long nb_delay_prev_time = 0;
if(millis() >= nb_delay_prev_time + milliseconds) {
nb_delay_prev_time += milliseconds;
return true;
}
return false;
}
Downloads
Everything is on github: https://github.com/weigu1/lora_p2p_sx1276_esp.
Interesting links
- WEMOS PCB https://github.com/hallard/WeMos-Lora
- SmartyReader® board v2.2 https://www.weigu.lu/microcontroller/smartyReader_P1/index.html#link_5.
